扁平足の診かた
扁平足の概要と課題
「扁平足」は、明確な定義や診断に関する国際的なコンセンサスがなく、初期から終末期までの病態がわからないことが課題となっていました。そこで2020年にアメリカ足の外科学会が扁平足を「PCFD(Progressive Collapsing Foot Deformity)」に変更し、扁平足は変形の一要素であり、足・足関節全体が変形に関与しているとし、形態的な変化に焦点を絞りました。
その中で、変形のタイプを5病型の組み合わせにし、病期stageは変形が矯正可能か否かの2つに分けられました。
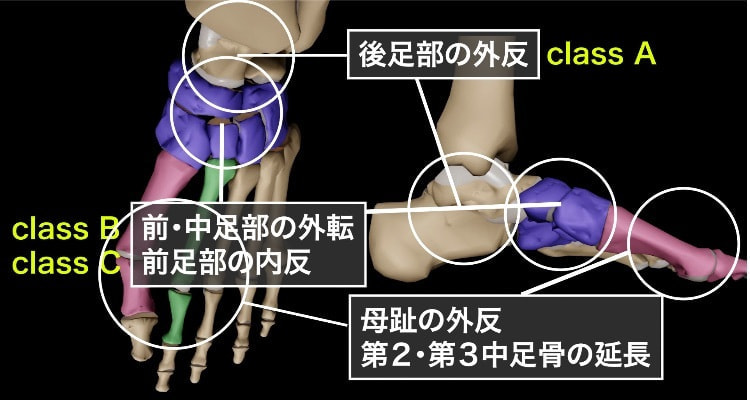
Class A : 後足部外反
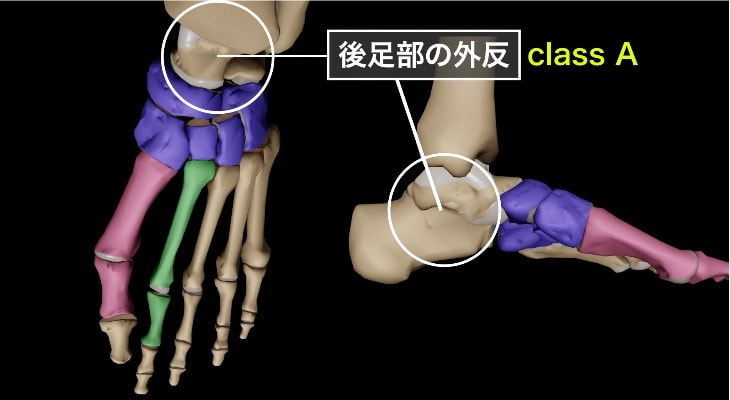
Class Aは、進行性足変形(PCFD)における「後足部外反」を特徴とする段階です。この状態では、以下のようなメカニズムで足の変形が進行します。
-
後足部の外反: 足のアーチが崩れることで、踵が外側に傾く現象です。これにより、足首の内側が低くなり、歩行時のバランスが不安定になります。
-
距踵関節の異常: 荷重がかかることで距踵関節が背屈し、外反することがClass Aの特徴です。このとき、距骨が踵骨に対して異常な位置にずれるため、周囲の靱帯や筋肉に負担がかかります。
-
インピンジメントの発生: 足が外反することで、距骨外側突起が踵骨と接触し、インピンジメント(衝突現象)が起こります。これにより、痛みや腫れ、可動域の制限が発生します。
-
生体力学的影響: 後足部の外反により、足部全体のバイオメカニクスが崩れます。歩行時に股関節の内転や膝の内向き(knee-in)が生じるため、下肢全体のアライメントにも悪影響を及ぼします。
Class B : 中足部・前足部外転
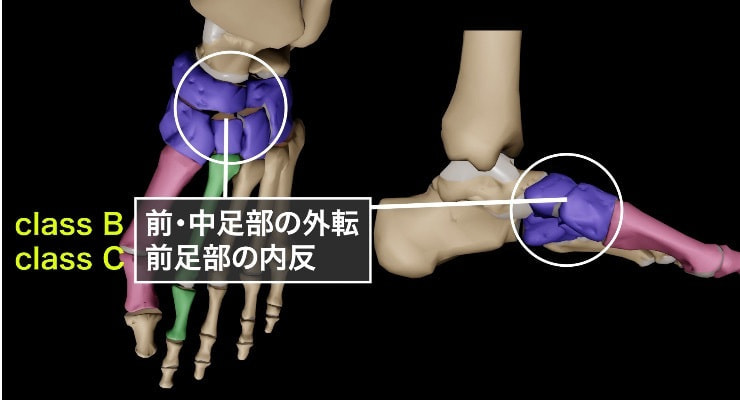
Class Bは、進行性足変形(PCFD)における「中足部・前足部外転」を特徴とする段階です。この状態では、足の前部が外側に向かって広がり、アーチの崩れが進行します。Class Bの特徴を以下に詳しく説明します。
-
前・中足部の外転: Class Bでは、足の前部および中部が外側に広がる外転変形が起こります。これにより、足のアーチがさらに低くなり、扁平足の進行が見られます。この段階では、特に距舟関節(足首の関節)が外転していることが観察されます。
-
距舟関節の関与: Class Bでは、距舟関節の不安定性が顕著になり、関節の外転が進行します。このとき、足のスプリング靱帯(内側縦アーチを支える靱帯)が損傷し、アーチの保持力が失われます。靱帯の断裂や伸長により、前足部の外転がさらに悪化します。
-
外側インピンジメント: 中足部・前足部の外転によって、距骨と踵骨の間でインピンジメント(衝突)が発生することがあります。これにより、足の外側に痛みが生じることが多く、歩行時の不快感や機能障害を引き起こします。
-
足部全体への影響: 前足部の外転は、足全体のアライメントを乱し、体重の負荷バランスを崩します。これにより、足底筋膜や周囲の組織に過度なストレスがかかり、さらなる変形を引き起こす可能性があります。
Class C : 前足部内反
Class Cは、進行性足変形(PCFD)における「前足部内反」を特徴とする段階です。この状態では、足の前部が内側に反ることでアーチが崩れ、足全体のバランスがさらに不安定になります。Class Cの特徴を以下に詳しく説明します。
-
前足部の内反: Class Cでは、足の前部が内側に反り上がる内反変形が見られます。この変形により、足のアーチが強調され、足の外側が持ち上がるため、歩行時に外側へ重心が偏りやすくなります。この状態は、足の前部が内側に捻られてしまうことで、足の機能が大幅に低下します。
-
第1中足趾関節の背屈: 前足部の内反は、第1中足趾関節が背屈(足の甲側に反る)することで起こります。この変形により、足の内側縦アーチが崩壊し、荷重時に足の外側へ圧力が集中します。この影響で、足底筋膜や周囲の筋・腱に負担がかかり、痛みや炎症を引き起こすことがあります。
-
足部アライメントの乱れ: Class Cでは、前足部の内反が起こることで、足全体のアライメントが乱れます。これにより、足の後部や中部にも影響が波及し、足部の他の関節や靱帯にもストレスがかかります。また、内反により足のバランスが不安定になるため、歩行時に足関節のねじれや転倒のリスクが高まります。
-
他のクラスとの関連: Class Cは、Class A(後足部外反)やClass B(中足部・前足部外転)と組み合わさることが多く、PCFD全体の進行に影響を及ぼします。特に、Class Bでの中足部・前足部の外転が進行すると、前足部の内反が強調され、Class Cの病態へと移行します。
Class D(距骨周囲亜脱臼)、Class E(距腿関節不安定症)は他の病態と重複する概念であるが、未だ病態解明されていないクラスと言ってもいいのかもしれません。
参考論文:
文献
- Key JA: Partial rupture of the tendon of the posterior tibial muscle. J Bone Joint Surg 35-
- Lapidus PW et al: Chronic non-specific tenosy-novitis with effusion about the ankle; report of three cases. J Bone Joint Surg 32-A : 175—179, 1950
- Johnson KA et al: Tibialis posterior tendon dysfunction. Clin Orthop Relat Res 239 : 196-
- Myerson MS: Adult acquired flatfoot defor-mity; treatment of dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon. Instr Course Lect 46: 393-405,1997
- Bluman EM et al: Posterior tibial tendon rup-ture; a refined classification system. Foot Ankle Clin 12 : 233-249, 2007
- Toolan BC et al : Complex reconstruction for the treatment of dorsolateral peritalar subluxation of the foot; early results after distraction arthrodesis of the calcaneocuboid joint in conjunction with stabilization of, and transfer of the flexor digitorum longus tendon to, the mid-foot to treat acquired pes planovalgus in adults. J Bone Joint Surg 1-A : 1545-1560,1999
- Deland JT et al: Posterior tibial tendon insufficiency ; which ligaments are involved? Foot Ankle Int 26: 427-435, 2005
- Gazdag AR et al: Rupture of the posterior tibial tendon; evaluation of injury of the spring ligament and clinical assessment of tendon transfer and ligament repair. J Bone Joint Surg 79-A : 675-681, 1997
- Deland JT : The adult acquired flatfoot and spring ligament complex ; pathology and implications for treatment. Foot Ankle Clin 6 : 129—135, 2001
- Brodell JD Jr et al : Deltoid-spring ligament reconstruction in adult acquired flatfoot deformity with medial peritalar instability. Foot Ankle Int 40 : 753-761, 2019
- Myerson MS et al: Classification and nomen-clature; progressive collapsing foot deformity. Foot Ankle Int 41 : 1271-1276, 2020
- Lee HY et al: Intra-and interobserver reliability of the new classification system of progressive collapsing foot deformity. Foot Ankle Int 43 : 582-589, 2022
- Li S et al: Diagnostic accuracy of the progressive collapsing foot deformity (PCFD) classifi-cation. Foot Ankle Int 43 : 800-809, 2022
- MacDonald A et al: Peritalar kinematics with combined deltoid-spring ligament reconstruction in simulated advanced adult acquired flatfoot deformity. Foot Ankle Int 41 : 1149—1157, 2020
- Henry JK et al: The foot and ankle kinematics of a simulated progressive collapsing foot deformity during stance phase; a cadaveric study. Foot Ankle Int 43 : 1577—1586, 2022
- Femino JE et al: The effect of progressive lateral column lengthening in a novel stage II-B flatfoot cadaveric model evaluated using software-guided radiographic measurements of foot alignment. Foot Ankle Int 43: 1099-1109, 2022
- Burssens A et al: Interaction of loading and ligament injuries in subtalar joint instability 2n ictering computed quantified by 3D weightbearing computed tomography. J Orthop Res 40: 933-944, 2022
- Louie PK et al: Talonavicular joint coverage and bone morphology between different foot types. J Orthop Res 32: 958-966, 2014
- Ferri Met al: Weightbearing CT scan of severe flexible pes planus deformities. Foot Ankle Int 29 : 199-204, 2008
- Yoshioka N et al : Weight-bearing three-dimensional computed tomography analysis of the forefoot in patients with flatfoot deformity.J Orthop Sci 21 : 154-158, 2016
- Kido M et al: Load response of the tarsal bones in patients with flatfoot deformity ; in vivo 3D study. Foot Ankle Int 32 : 1017-1022, 2011
- Kido M et al: Load response of the medial longitudinal arch in patients with flatfoot deformity ; in vivo 3D study. Clin Biomech 28 :
- Apostle KL et al: Subtalar joint axis in patients with symptomatic peritalar subluxation compared to normal controls. Foot Ankle Int 35 :
- Lalevée M et al: Prevalence and pattern of lateral impingements in the progressive collapsing foot deformity. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 143: 161-168, 2023
- Jeng CL et al : Assessment of bony subfibular impingement in flatfoot patients using weight-bearing CT scans. Foot Ankle Int 40 : 152-158,2019
- Lintz F et al: Diagnostic accuracy of measurements in progressive collapsing foot deformity using weight bearing computed tomography ; a matched case-control study. Foot Ankle Surg 28: 912-918, 2022
- Arena CB et al: Assessment of hindfoot alignment comparing weightbearing radiography to weightbearing computed tomography. Foot
- Ankle Int 42 : 1482-1490, 2021
- Kim J et al: Radiographic cutoff values for predicting lateral bony impingement in progressive collapsing foot deformity. Foot Ankle Int 43 : 1219—1226, 2022
- Bakshi N et al: Association between hindfoot alignment and first metatarsal rotation. Foot Ankle Int 43 : 105-112, 2022
- Dibbern KN et al: Three-dimensional distance and coverage maps in the assessment of peri-talar subluxation in progressive collapsing foot deformity. Foot Ankle Int 42: 757—767, 2021
- Barbachan Mansur NS et al: Association between middle facet subluxation and foot and ankle offset in progressive collapsing foot deformity. Foot Ankle Int 43: 96-100, 2022
- de Cesar Netto C et al : Combined weightbear-ing CT and MRI assessment of flerible non22) Auch E et al: Distal tibiofibular syndesmotic widening in progressive collapsing foot defor-mity. Foot Ankle Int 42 : 768-775, 2021
- Dagneaux L et al: Three-dimensional biometrics to correlate hindfoot and knee coronal alignments using modern weightbearing imag-ing. Foot Ankle Int 41 : 1411—1418, 2020
- Wang Z et al : Towards patient-specific medi-alizing calcaneal osteotomy for adult flatfoot ; a finite element study. Comput Methods Bio-mech Biomed Engin 21 : 332-343, 2018
- Malakoutikhah H et al: The contribution of the ligaments in progressive collapsing foot defor-mity; a comprehensive computational study. J
- Orthop Res 40: 2209—2221, 2022
- Cody EA et al: Correlation of talar anatomy and subtalar joint alignment on weightbearing computed tomography with radiographic flatfoot parameters. Foot Ankle Int 37: 874-881,
- Shin HS et al: Flatfoot deformity affected the kinematics of the foot and ankle in proportion to the severity of deformity. Gait Posture 72 : 123—128, 2019
- Wang C et al : Pathological kinematic patterns of the tarsal complex in stage Il adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. J Orthop Res 37 :
- 477—482, 2019
- Ellis SJ et al: New radiographic parameters assessing forefoot abduction in the adult acquired flatfoot deformity. Foot Ankle Int 30: 1168—1176, 2009
- Thordarson DB et al : Dynamic support of the human dynamic support of the human longitudinal arch; a biomechanical evaluation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 316: 165—172, 1995
- Kokubo T et al : Effect of the posterior tibial and effect of the posterior tibial and peroneal longus on the mechanical properties of the foot arch. Foot Ankle Int 33 : 320—325, 2012
- Jotoku T et al: Anatomy of ligamentous structures in the tarsal sinus and canal. Foot Ankle Int 27: 533-538,2006
- Kelikian AS et al : Sarrafian's Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle; Descriptive, Topographic, Functional, 3rd ed, Lippincott Williams &Wilkins, 120—127, 2011
- Flores DV et al: Adult acquired flatfoot defor-mity; anatomy, biomechanics, staging, and imaging findings. Radiographics 39: 1437-1460, 2019
- Nosewicz TL et al : Radiological morphology of peritalar instability in varus and valgus tilted ankles. Foot Ankle Int 35: 453-462, 2014
- Wang B et al : Does the subtalar joint compensate for ankle malalignment in end-stage ankle arthritis? Clin Orthop Relat Res 473 : 318-325, 2015
- Imai K et al: Features of hindfoot 3D kinetics in flat foot in ankle-joint maximal dorsiflexion and plantarflexion. J Orthop Sci 16 : 638-643,
- Maeda Het al: A kinematic and kinetic analysis of the hip and knee joints in patients with posterior tibialis tendon dysfunction ; comparison with healthy age-matched controls. Gait Posture 66 : 228-235, 2018
- Steiner CS et al: Combined subtalar and navic-ulocuneiform fusion for treating adult acquired
- flatfoot deformity with medial arch collapse at the level of the naviculocuneiform joint. Foot Ankle Int 40: 42-47, 2019
- de Asla RJ : Biomechanics of the foot and ankle. Orthopaedic Knowledge Update ; Foot and Ankle (ed by Chou LB), 6th ed, Wolters Kluwer, 6, 2020

